
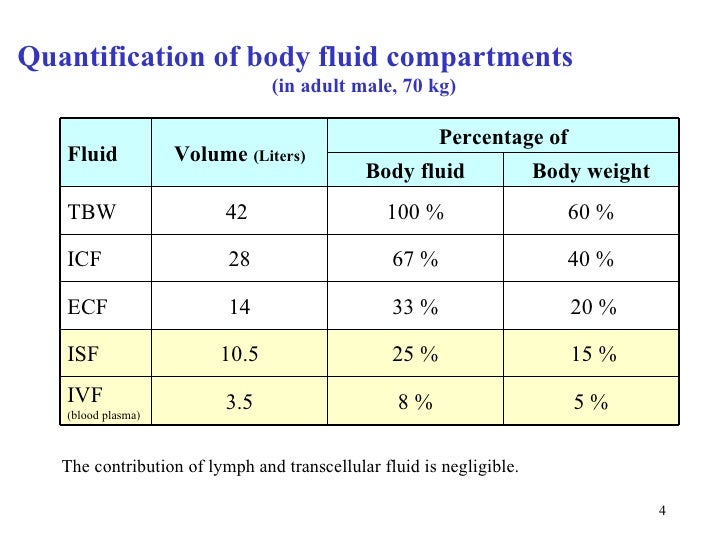
Approximately 20 percent of the ECF is found in plasma. The ECF accounts for the other one-third of the body’s water content. The second largest volume is the interstitial fluid, which surrounds cells that are not blood cells. Most of the water in the body is intracellular fluid. If the amount of water inside a cell falls to a value that is too low, the cytosol becomes too concentrated with solutes to carry on normal cellular activities if too much water enters a cell, the cell may burst and be destroyed.įigure 3. This fluid volume tends to be very stable, because the amount of water in living cells is closely regulated. The ICF makes up about 60 percent of the total water in the human body, and in an average-size adult male, the ICF accounts for about 25 liters (seven gallons) of fluid. The ICF lies within cells and is the principal component of the cytosol/cytoplasm. Extracellular fluid has two primary constituents: the fluid component of the blood (called plasma) and the interstitial fluid (IF) that surrounds all cells not in the blood. Extracellular fluid (ECF) surrounds all cells in the body. The intracellular fluid (ICF) compartment is the system that includes all fluid enclosed in cells by their plasma membranes. Materials travel between cells and the plasma in capillaries through the IF.īody fluids can be discussed in terms of their specific fluid compartment, a location that is largely separate from another compartment by some form of a physical barrier. Blood plasma is the second part of the ECF. The interstitial fluid (IF) is part of the extracellular fluid (ECF) between the cells. The intracellular fluid (ICF) is the fluid within cells. An appropriate balance of solutes inside and outside of cells must be maintained to ensure normal function.

As a result, water will move into and out of cells and tissues, depending on the relative concentrations of the water and solutes found there. Osmosis is basically the diffusion of water from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration, along an osmotic gradient across a semi-permeable membrane. In the body, water moves through semi-permeable membranes of cells and from one compartment of the body to another by a process called osmosis. For instance, sodium ions (Na +) and chloride ions (Cl –) are often referred to as electrolytes. Often in medicine, a mineral dissociated from a salt that carries an electrical charge (an ion) is called and electrolyte. In the human body, solutes vary in different parts of the body, but may include proteins-including those that transport lipids, carbohydrates, and, very importantly, electrolytes. The dissolved substances in a solution are called solutes. The chemical reactions of life take place in aqueous solutions. Identify the causes and symptoms of edema.Explain the importance of protein channels in the movement of solutes.Contrast the composition of the intracellular fluid with that of the extracellular fluid.Explain the importance of water in the body.Otherwise, the venous blood pools in the lower limbs and can leak into surrounding tissues.By the end of this section, you will be able to: This is because deep veins in the lower limbs rely on skeletal muscle contractions to push on the veins and thus “pump” blood back to the heart. Mild, transient edema of the feet and legs may be caused by sitting or standing in the same position for long periods of time, as in the work of a toll collector or a supermarket cashier.

An allergic reaction can cause capillaries in the hand to leak excess fluid that accumulates in the tissues.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
